Code P0325 - Knock Sensor Malfunction (Sensor 1, Bank 1): Symptoms, Causes, Common Problems, Diagnostic
By Vlad Samarin, March 30, 2024
The OBDII trouble code P0325 - Knock Sensor Malfunction (Sensor 1, Bank 1) indicates an issue with the knock sensor
in the engine. The knock sensor is essentially a microphone that is bolted to the engine. Its primary function is to detect abnormal knocking noises in the
engine, typically caused by detonation or pre-ignition.
Symptoms:
When a knock sensor malfunctions, there could be no symptoms at all, or some of the following symptoms might be present:
- Check Engine Light stays ON
- Decreased engine performance
- Engine knocking or pinging
- Poor fuel economy
Causes:
- Faulty knock sensor
- Damaged or corroded knock sensor wiring
- Moisture entering the knock sensor or its wires
- Loose or damaged knock sensor connector
- Engine mechanical problems
- The air/fuel mixture is too lean
- PCM software needs to be updated
- Problem with the PCM connector or PCM itself
Common Problems:
Common problems associated with the P0325 code include:One thing we have seen many times is that the wiring harness that goes to the knock sensor gets damaged by rodents. This is especially common in V6/V8 engines, where the knock sensor is located in the valley between the cylinder banks. Typically, you will see signs of chewed isolation material, seeds and chewed wires.
In some cases, the damaged wires can be repaired, in others, the knock sensor wiring harness or engine harness will have to be replaced. In some cases, such damage can be covered by the car insurance.
A failed knock sensor is also fairly common. For example, in older Honda CR-Vs with the 2.4L engine, the code P0325 is commonly caused by a bad knock sensor. It's located under the intake manifold.
We also found a number of service bulletins from various car makers that recommend updating the PCM software if the code P0325 is present. That's why checking for service bulletins is important when diagnosing this code.
Diagnostic:
Diagnosing the P0325 code typically involves the following steps: First, are there any other codes? If there are other trouble codes, such as P0171 or P0341, they will need to be diagnosed and repaired first.If there are no other codes, are there any abnormal knocking noises, such as piston slap, timing chain rattle, or others, coming from the engine? Is there enough oil? Any engine mechanical problems that could potentially cause the code P0325 will need to be addressed first.
Check for manufacturer's service bulletins for the code P0325. We found a number of service bulletins for this code, and several of them recommend updating the PCM software.
If there are no other codes and the engine sounds normal, the next step is to clear the code and see if it comes back after driving.
If the code comes back, the next step is to visually check the knock sensor wiring and connector for signs of damage or corrosion.
Advertisement
It's also helpful to research common problems for the Year Make and Model of your vehicle that can cause this code. For example, we found many YouTube videos pointing to a bad knock sensor as a cause of the code P0325 in older Honda vehicles with a 2.4L engine
If nothing obvious is found, the knock sensor and the wiring between the knock sensor and the PCM will need to be checked as per the service manual for the vehicle.
For example, for some cars, the service manual may suggest checking the voltage at the knock sensor connector or testing the wires between the knock sensor and the PCM for continuity. For other cars, the resistance of the knock sensor may need to be measured and compared to specs.
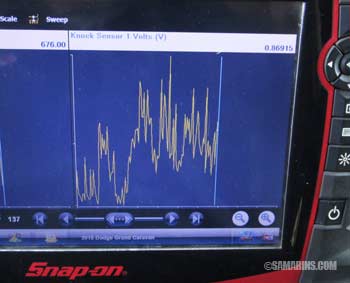
The service manual may suggest checking the knock sensor signal with a scan tool. For example, this photo shows a normal signal of a working knock sensor with an engine running (KOER) on the scan tool screen.
The repair will depend on the diagmosis.
Repair
If the knock sensor itself is found to be bad, the part is not expensive, however, it may be a bit difficult to replace due to its location. Typically, the knock sensor is bolted to the cylinder block; often, it's located under the intake manifold.When replacing the knock sensor, it's important to tighten the bolt that holds it to the specified torque in order for the sensor to work properly.
If the sensor wiring is found to be damaged, it will need to be repaired or replaced. We know cases where the sensor wiring was found to be damaged by rodents, and the insurance covered the repairs.
If the knock sensor code is suspected to be caused by a mechanical problem with the engine, such as, for example, a stretched timing chain, it will need to be repaired first.
The Role of a Knock Sensor:
A knock sensor is a crucial component of a car's engine management system. It's essentially a microphone that is bolted to the engine cylinder block. It detects the presence of abnormal engine noise known as "knocking" or "pinging," which occur when the air-fuel mixture ignites prematurely (detonates) in the combustion chamber. This process is known as "pre-ignition" or "detonation" and it happens when the ignition timing is advanced too far for the fuel that is used.The engine computer (PCM) wants to keep the ignition timing as advanced as possible without causing detonation. If detonation occurs, the knock sensor sends the signal to the engine computer (PCM) and in response, the PCM retards the ignition timing for best performance without detonation.